2376-0249
Medical Image - International Journal of Clinical & Medical Images (2015) Volume 2, Issue 3
Author(s): Ramachandra Reddy VJ*, Chidanand GC and Manjunath CN
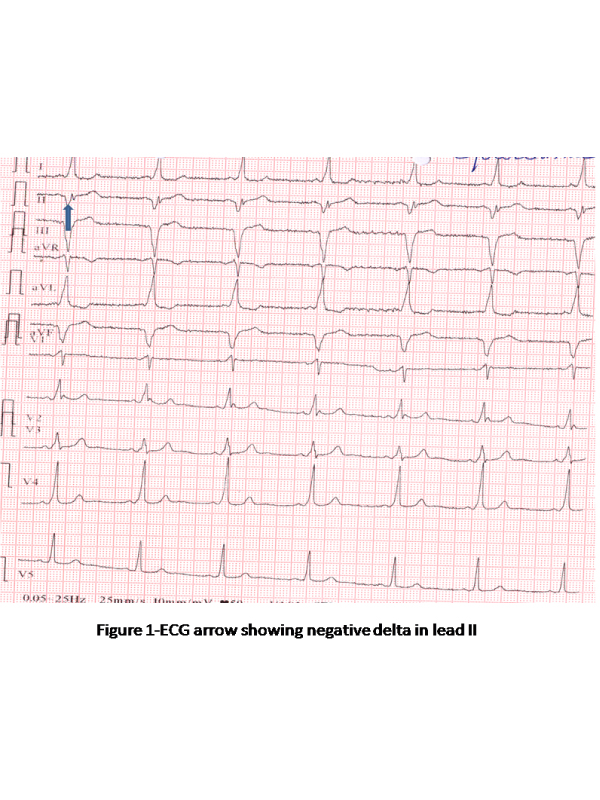
Subepicardial posteroseptal accessory pathways, which consist of accessory pathway (AP) required ablation from within the subepicardial venous system, including the middle cardiac vein and other coronary veins [1]. As the electrocardiogram (ECG) algorithm accurately localizes accessory pathways prior to ablation, it may help the physician advice the patient regarding the likelihood of success and complications of the procedure. The ECG algorithm may aid selection of patients in whom coronary sinus angiography should be perfomied in order to delineate its anatomy, thus allowing mapping in the coronary veins and anomalous structures of the coronary sinus. A negative delta wave in lead II identifies the subepicardial posteroseptal accessory pathway as per Arudas criteria [2]. We report a Electrocardiogram manifest of classic subepicardial pathway arising from middle cardiaac vein.
We report a 50years old lady presented with history of recurrent palpitations of 2 years duration.No past history of any cardiac disease. Baseline ECG (Figure 1) showed evidence of pre- excitation with positive delta wave in leads I, AVL, V1-V6 with negative delta wave in leads II, III, AVF. A distinctive ECG clue for the presence of an epicardial AP was a steeply negative delta wave in lead II.Electrophysiological studies confirmed subepicardial pathway arising from middle cardiac vein and successful ablation of the pathway done.Since we localized the pathway as epicardial pathway on ECG by applying Arudas criteria, coronary venous sinus angiography done and ablated by left sided approach by transseptalpuncture, stressing importance of ECG localization.
 Awards Nomination
Awards Nomination

