2376-0249
Clinical-Medical Image - International Journal of Clinical & Medical Images (2016) Volume 3, Issue 3
Author(s): Haruki Funao and Takahiro Koyanagi
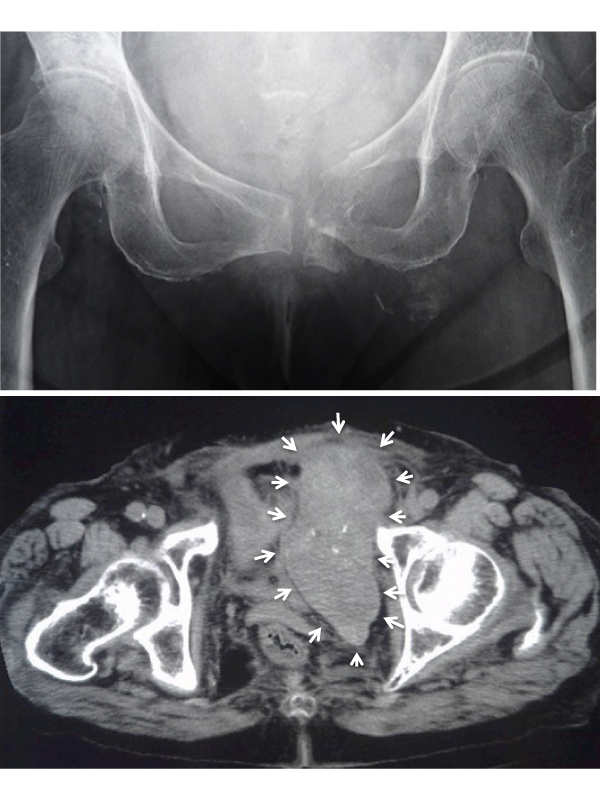
Figure 1: Displaced left pubic ramus fracture.
Figure 2: Massive intrapelvic hematoma (axial size, 11 cm by 5 cm) around the fracture site.
An 88-year-old female presented with a left thigh pain and dysuria. She visited our hospital 2 week after she noticed her symptoms. She stated that she might have a low-energy fall, but she could not identify the exact onset. Her radiograph of the pelvis (Figure 1) showed displaced left pubic ramus fracture. Her computed tomographic scanning of the pelvis (Figure 2) showed massive intrapelvic hematoma (axial size, 11 cm by 5 cm) around the fracture site, although she did not use any anticoagulants. Because her bone mineral density was 0.357 g/cm2 , and T score was -4.8 SD, she started a bisphosphonate therapy. She received a bed-rest physical therapy for 6 weeks, and the hematoma regressed spontaneously. She started full weight bearing after 6 weeks, and walked by a walker after 8 weeks. Although it is extremely rare to develop massive chronic intra-pelvic hematoma after a lowenergy pubic ramus fracture without any use of anticoagulants, it may occur in elderly and severely osteoporotic patient.
 Awards Nomination
Awards Nomination

