2376-0249
Clinical-Medical Image - International Journal of Clinical & Medical Images (2022) Volume 9, Issue 9
Author(s): Molly Menser*
Epiphany Dermatology, Kansas City University, USA
Date of Submission: 12 September, 2022, Manuscript No. ijcmi-22-78947; Editor assigned: 13 September, 2022, PreQC No. P-78947; Reviewed: 19 September, 2022, QC No. Q-78947; Revised: 22 September, 2022, Manuscript No. R-78947; Published: 30 September, 2022, DOI: 10.4172/2376-0249.1000850
Citation: Menser M. (2022) Non-surgical Treatment of Large Ulcerated Basal Cell Carcinoma. Int J Clin Med Imaging 9:850.
Copyright: © 2022 Menser M. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
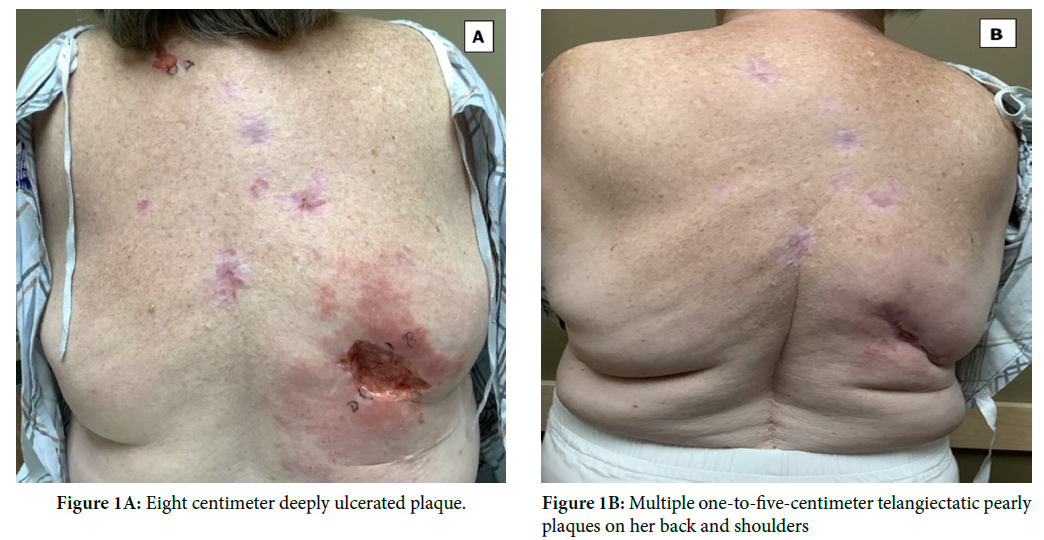
A 68-year-old female with a history of basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and melanoma presented to the outpatient clinic with non-healing ulcerations. Physical exam showed an eight centimeter deeply ulcerated plaque as well as multiple one-to-five-centimeter telangiectatic pearly plaques on her back and shoulders. A biopsy of the larger lesion revealed infiltrative BCC with prominent squamous differentiation. Biopsies of additional lesions were consistent with these findings. Wide local excision is standard of care; however, vismodegib 150 mg PO daily was recommended due to the extensive nature and multiple locations. Vismodegib competitively inhibits Smoothened protein, deactivating the Hedgehog pathway. It is indicated in patients not suitable for surgery, topical treatment, or radiation therapy due to locally advanced or metastatic BCC. The patient noted significant nausea and hair loss at a sixteen-week follow-up appointment and her lesions were markedly decreased in size and shallower. Unfortunately, she was lost to follow-up (Figure 1A and 1B).
Basal cell carcinoma; Melanoma
 Awards Nomination
Awards Nomination

