2376-0249
Case Blog - International Journal of Clinical & Medical Images (2015) Volume 2, Issue 7
Author(s): Piloni V*
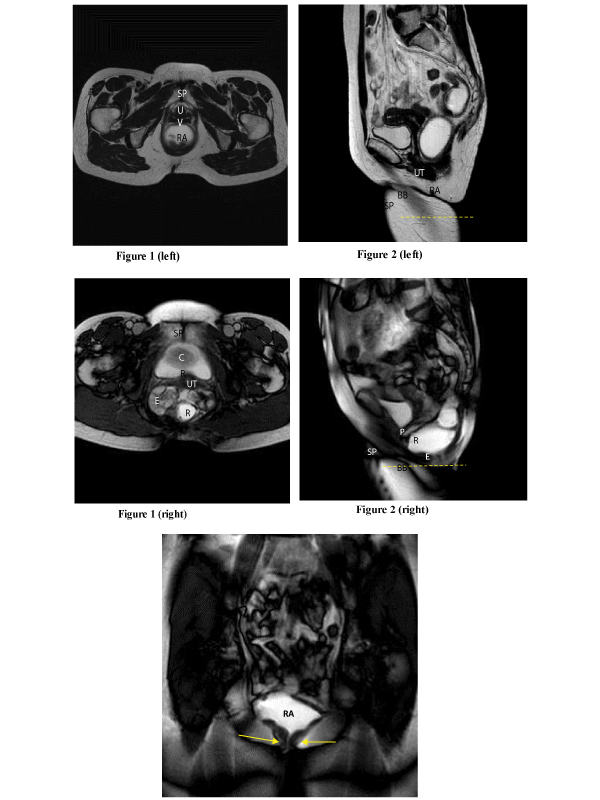
Figure 1: 59-year old woman with occasional symptoms of ODS of recent onset, mucous prolapsed and no rectocele at physical examination. MR Axial balance fast field echo (BFFE) pulse sequence taken at the same level of pubic symphysis in steady-state at rest (left) and on Valsalva maneuver (right) (TR/TE,3/1.5 msec; FA, 45°; thickness, 10 mm; FOV 300 mm; Matrix 256x256; acq. time, 9 sec; Nex,2). On straining, marked ballooning of the levator hiatus with a + 43% increase in the longitudinal diameter and +96% increase in the transverse diameter within which there are cystocele (C), enterocele (E) and rectocele (R) , and prolapsed uterine cervix (UT); SP, symphysis pubis; V, vagina; U, urethra; RA, rectal ampulla.
Figure 2: MR Sagittal BFFE fast imaging (TR/TE, 2.7/1.3 msec; FA, 45°, thickness 30 mm, Matrix 256x256; FOV 300 mm; acq.time 43 sec; Nex,2; tot. im, 50, 1m/sec 1/0.8 sec) obtained at the beginning (left) and after repeated attempts during expulsion (right) of rectal content (acustic gel): clear depiction of 31.5 mm deep rectocele (R), enterocele (E), peritoneocele (P), and bladder base (BB) descent well below the hymen plane (dotted line); SP, symphysis pubis; RA, rectal ampulla; UT, uterus.
Figure 3: MR coronal BFFE fast imaging (TR/TE, 2.8/1.3 msec; FA, 45°; thickness 30 mm, Matrix 256x256; FOV 300 mm; acq time, 44 sec; Nex, 2; tot im, 50; im/ sec 1/0.8 sec): lack of anal widening (arrows) during rectal expulsion consistent with anal sphincter hypertone, prolonged evacuation time (>4 min) and retention of contrast in a dilated rectal ampulla (RA).
 Awards Nomination
Awards Nomination

