2376-0249
e-poster Presentation - International Journal of Clinical & Medical Images (2015) Volume 2, Issue 6
Author(s): Jaml TR*
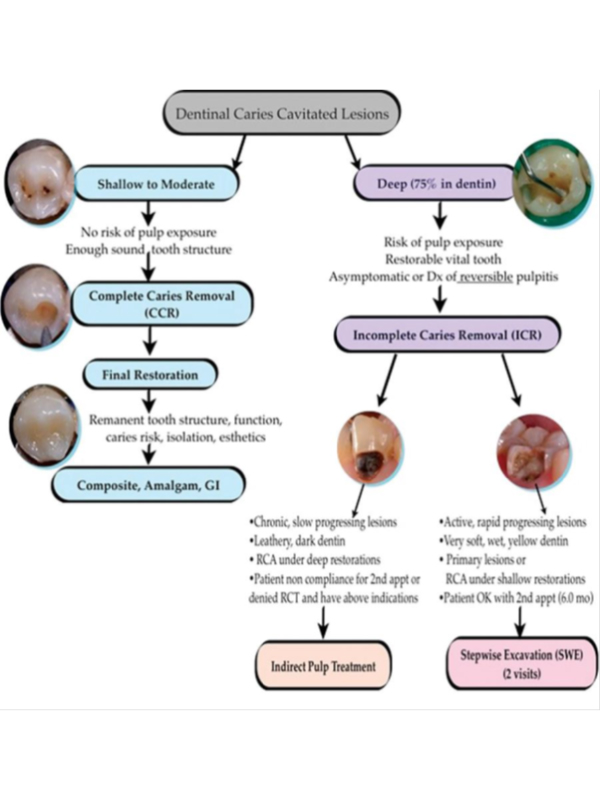
Operative dentistry not only requires technical expertise and an in-depth understanding of materials science, but knowledge in cariologyand pulp biology is also essential. Treatment of deep caries lesions approaching a healthy pulp presents a significant challenge to the practitioner. The traditional management of carious lesions of any kind dictates the removal of all infected and affected dentin to prevent further cariogenic activity and provide a well–mineralized base of dentin for restoration. Pulp vitality is extremely important for the tooth viability, since it provides nutrition and acts as biosensor to detect pathogenic stimuli. In 1938, Bodeckerintroduced the Stepwise Excavation technique for treatment of teeth with deep caries for preservation of pulp vitality and conservative. Stepwise Excavation has gained a growing interest in the recent years from different researchers due to advances made in techniques and dental materials with good sealing ability and antibacterial properties. Clinical study on stepwise excavation of deep carious lesions in vital permanent teeth: a 12-month follow-up study shown this technique is a conservative community based treatment.
 Awards Nomination
Awards Nomination

