2376-0249
Medical Image - International Journal of Clinical & Medical Images (2015) Volume 2, Issue 3
Author(s): Ramachandra Reddy VJ*, Chidanand GC and Manjunath CN
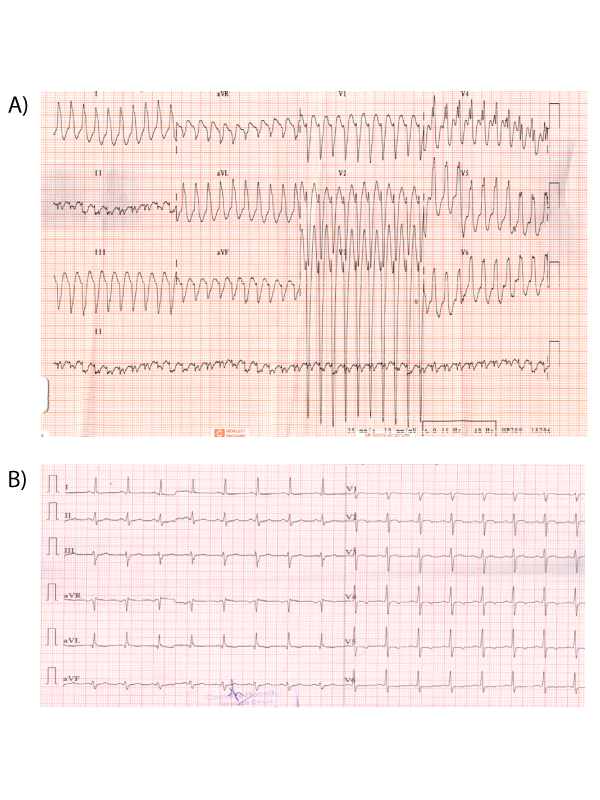
Patients who present with wide complex tachycardia are always challenging both diagnostically and therapeutically. Mahaim fiber is an uncommon cause of tachycardia in which cardiac pre-excitation occurs via slow-conducting, long accessory pathways that terminate in the right ventricular free wall or into the adjacent right bundle. It was first reported by Mahaim and Bennett in 1937, subsequently, other investigators have elucidated the electrophysiological properties of this pathway. We report a 45 years old man presented to the emergency department with history of sudden onset palpitations associated with fatigue. He was known case of diabetes mellitus and hypertension.Twelve leads electrocardiogram was suggestive of narrow QRS regular tachycardia with left bundle branch block (LBBB) morphology,left axis deviation with late transition of QRS in precordial leads in V5 (Figure 1). Patient was hemodynamically stable and was given intravenous adenosine. Subsequently 2D transthoracic echocardiogram revealed normal study. Baseline electrocardiogram showed normal sinus rhythm with no septal q waves in left precordial leads and rS pattern in lead III (Figure 2) typical of Mahaim tachycardia. Electrophysiologic study then confirmed the diagnosis of Mahaim fiber tachycardia. Treatment was successful with mapping of the accessory pathways followed by radiofrequency ablation. In this situation, clinicians must not administer agents that slow conduction through the AV node, as this makes conduction via the accessory pathway more likely and results in immediate hemodynamic collapse, ventricular fibrillation, or death.
 Awards Nomination
Awards Nomination

